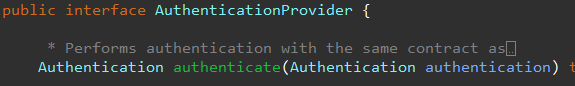
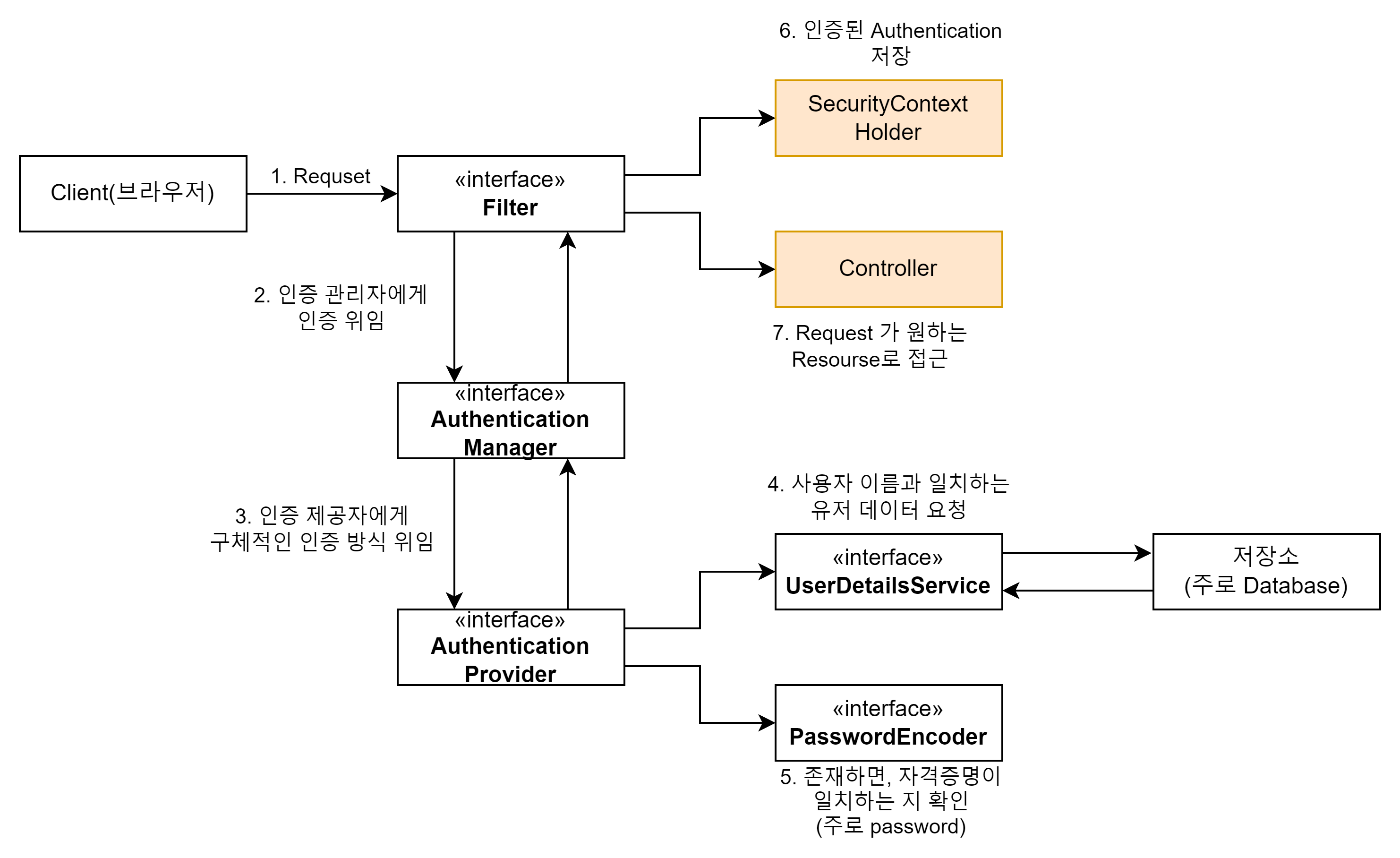
AuthenticationProvider 인터페이스가 인증 논리를 담당한다.
AuthenticationProvider의 이해
실제 인증은 여러 방식이 있을 수 있다.
단순한 id/pw 인증이 전부가 아니다.
스프링 시큐리티는 AuthenticationProvider 로 모든 인증을 추상화하고, 이게 맞게 구현만 하면 어떠한 인증 시나리오도 구축할 수 있다.
인증에 사용되는 Authentication
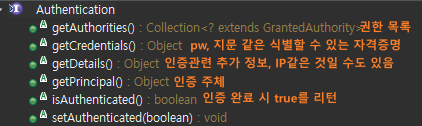
Authentication은 인증에 사용되는 필수 인터페이스다.
아래 처럼 인자로 사용되어 인증에 사용된다.
Authentication은 Principal 를 확장한다. Principal은 자바 시큐리티 인터페이스다.
인증 논리 구현
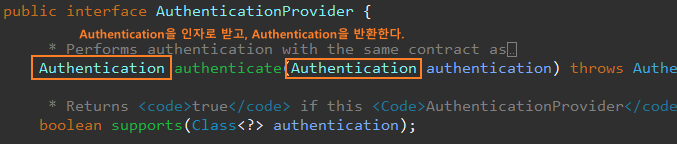
authenticate() 은 인증 성공 시 완전히 인증된 Authentication을 반환해야 한다.
isAuthenticated() true를 반환하고, 모든 필수 정보가 포함되야한다.
단, 보안 상의 이유로 자격증명은 제거될 수 있다.
인증이 이미 성공했기 때문에 더 이상 자격증명 같은 민감한 정보가 필요없기 때문이다.
supports() 는 매개변수 Authentication을 인증 시 사용할 수 있는지 여부를 리턴한다.
주의할 것은 이 메서드가 true를 리턴해도 authenticate()메서드에서 null을 리턴해 인증을 거부할 수 있다.
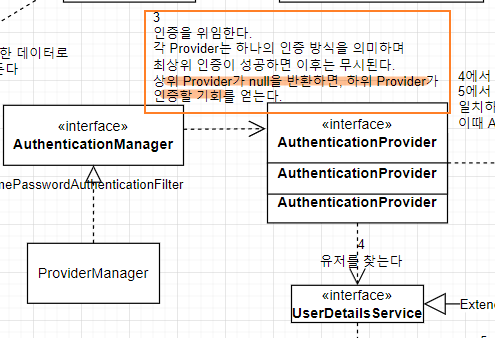
supports()가 false 경우 AuthenticaitonManager는 인증을 시도하지 않는다. 바로 다음 AuthenticationProvider에게 인증을 위임한다.
맞춤형 인증 논리 구현
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationProvider;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.BadCredentialsException;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class CustomAuthenticationProvider implements AuthenticationProvider{
Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());
@Autowired
private UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
@Autowired
private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
logger.info("=========== 인증 시작 ===========");
String username = authentication.getName();
String password = authentication.getCredentials().toString();
UserDetails userDetails = userDetailsService.loadUserByUsername(username);
if(passwordEncoder.matches(password, userDetails.getPassword())) {
return new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
username, password, userDetails.getAuthorities());
}
throw new BadCredentialsException("인증 실패");
}
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> authentication) {
return UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.class.isAssignableFrom(authentication);
}
}
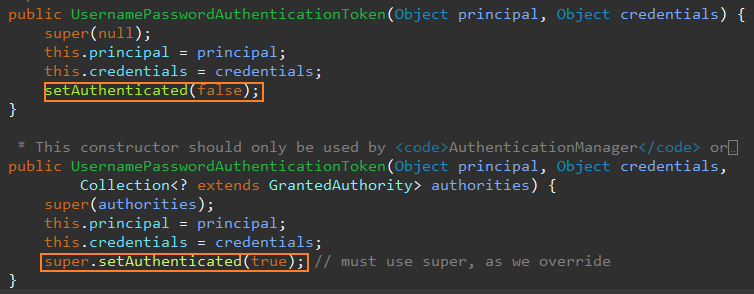
참고로 권한 정보까지 사용해서 UsernamepasswordAuthenticationToken을 생성하면
아래와 같이 완전히 인증됨을 의미하는 플래그 값을 true로 설정한다.
실행

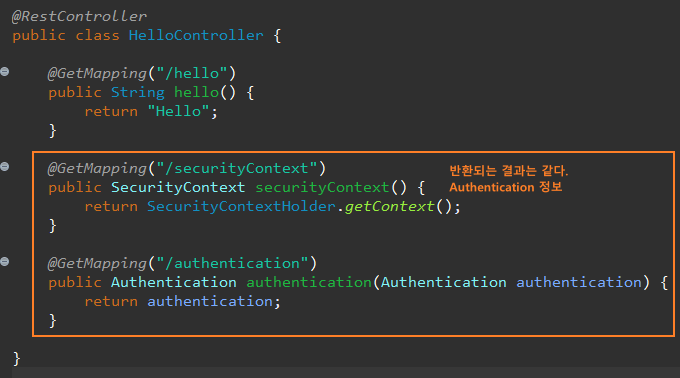
SecurityContext 이용
SecurityContext(이하 보안 컨텍스트)
인증 프로세스가 끝난 후 인증된 Authentication에 대한 세부 정보가 필요할 가능성이 크다.
주로 이름과 권한을 지속적으로 확인해야할 수 있다.
SecurityContext는 Authentication 객체가 요청이 유지되는 동안 내부에 저장한다.

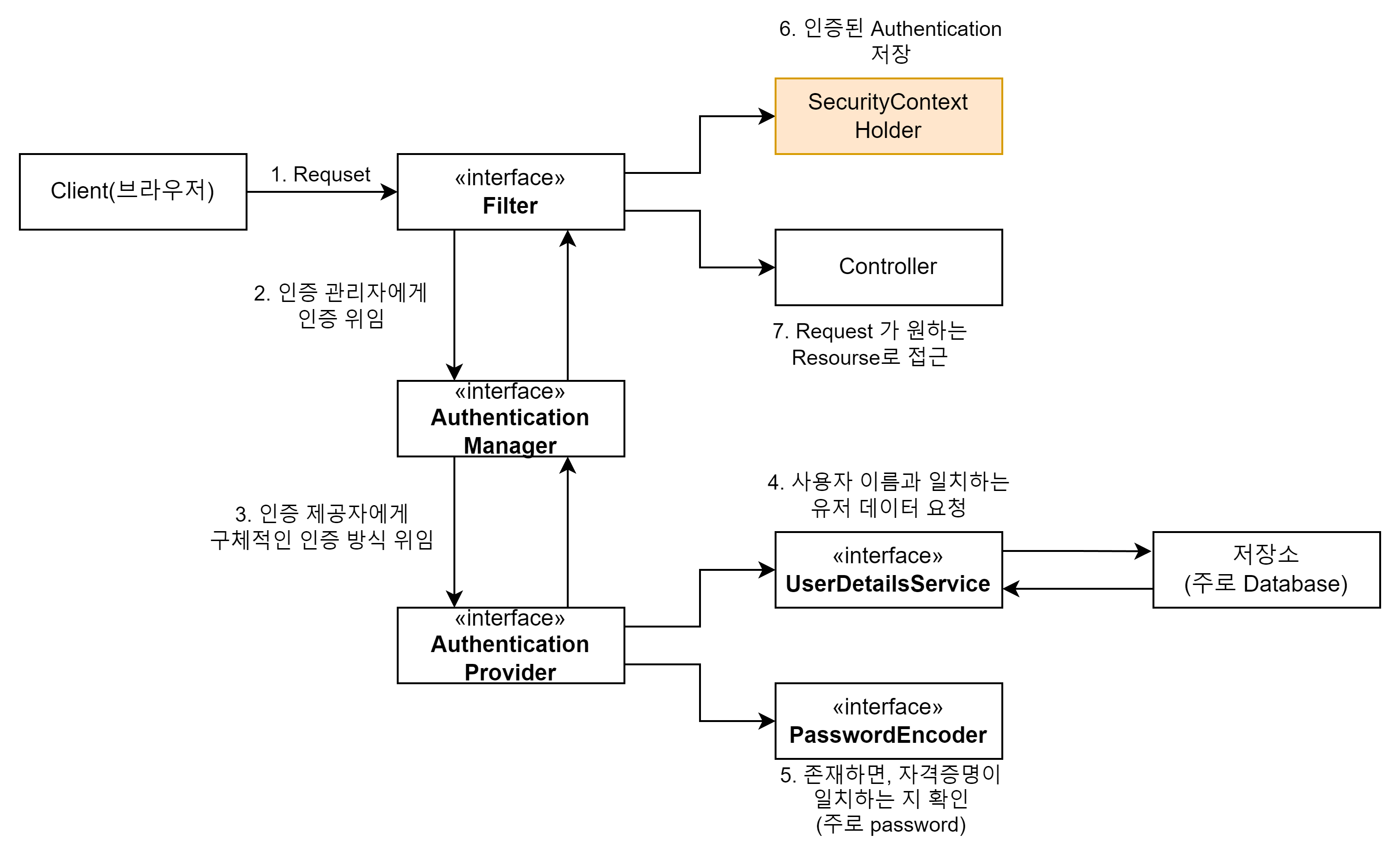
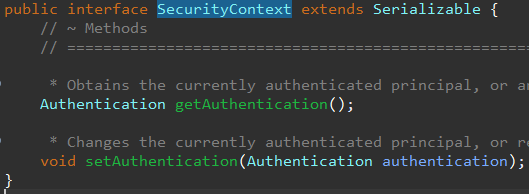
보안 컨텍스트는 이게 전부다. 보면 알 수 있듯 인증 객체를 저장하는 것이 역할이다.
보안 컨텍스트를 관리하는 SecurityContextHolder는 3 가지 모드를 지원한다.
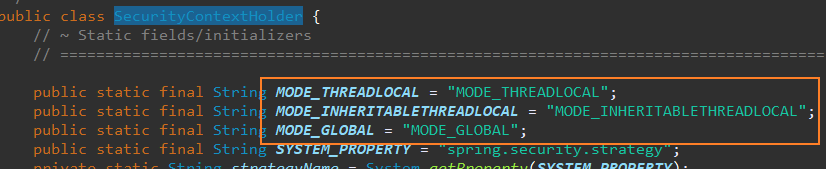
MODE_THREADLOCAL
스레드에 안전한 저장소에 보안 문맥을 저장한다.
일반적으로 WAS는 하나의 요청 당 하나의 쓰레드를 가지므로 기본이 되는 전략이다.
MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL
MODE_THREADLOCAL와 유사하다.
비동기 메서드의 경우, 다음 스레드로 복사해서 사용한다.
예를들어, @Async 메서드를 실행하는 새 스레드가 보안 컨텍스트를 상속한다.
MODE_GLOBAL
애플리케이션의 모든 스레드가 같은 보안 컨텍스트를 공유한다.
스프링 시큐리티는 이외에도 사용자가 커스텀한 전략을 사용하도록 설정할 수 있다.
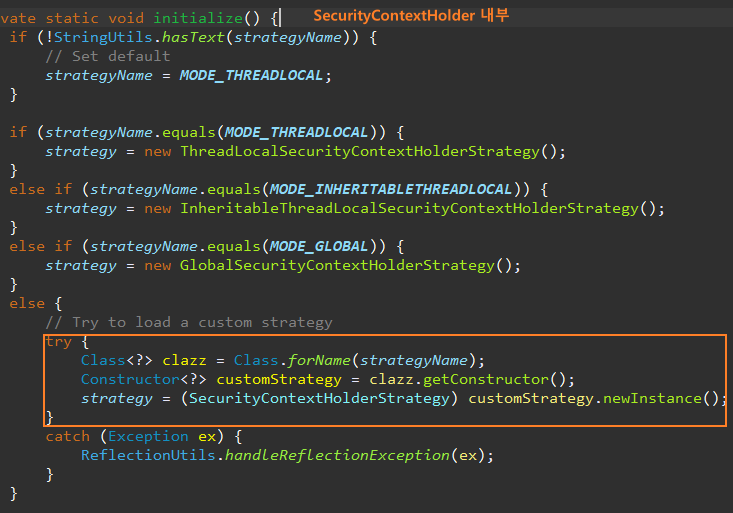
보안 컨텍스트를 위한 보유 전략 이용
MODE_THREADLOCAL
기본 전략은 MODE_THREADLOCAL 이다.
내부적으로 ThreadLocal 을 사용한다.
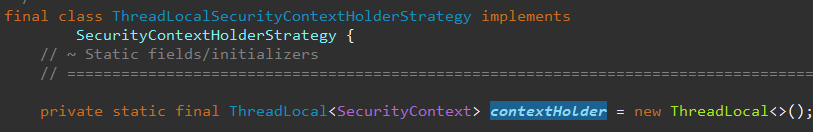
ThreadLocal 에 저장된 데이터는 다른 쓰레드에선 접근이 불가능하다.
이는 웹 요청마다 새로운 쓰레드를 생성하는 일반적인 WAS와 잘 맞아떨어지는 동작방식이다.
만약 서버가 비동기 기술을 사용한다면 문제가 될 수 있다. 기존 쓰레드에서 새로운 쓰레드를 생성해 실행하면, 새로 생성된 쓰레드는 접근을 하지 못하기 때문이다.
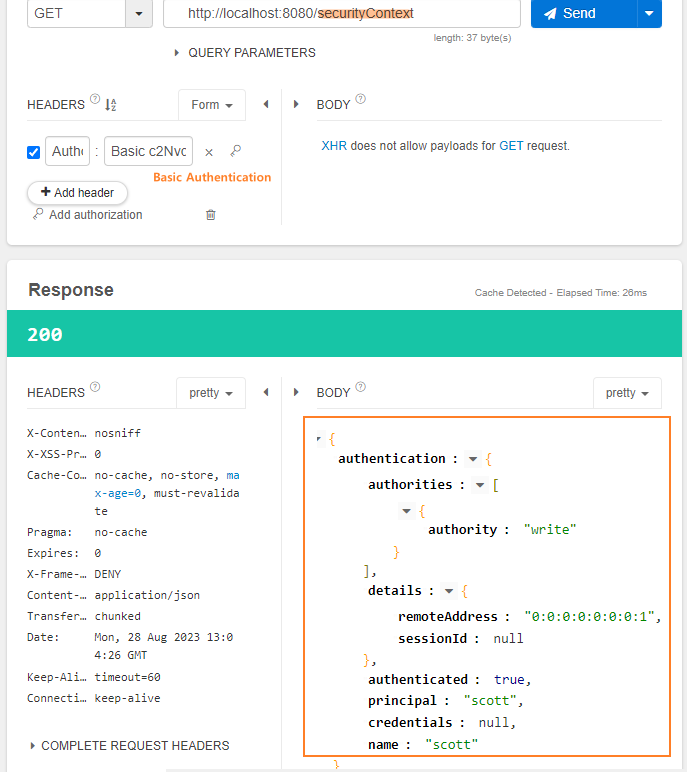
6번에 저장된 보안 컨텍스트를 7번에서 꺼내서 사용할 수 있다.
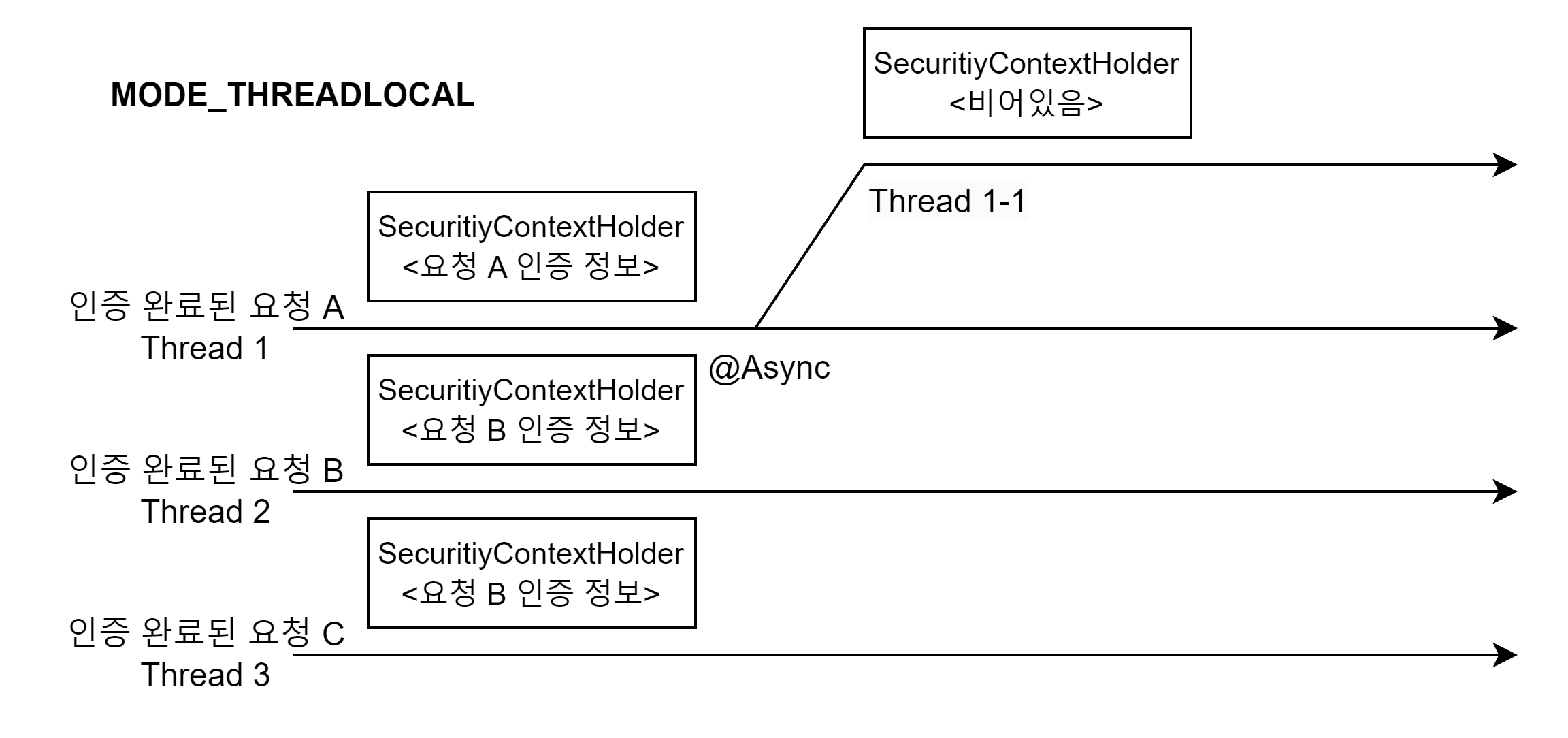
MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL
비동기를 사용하는 상황에서 전략
비동기 설정

아직 보안 컨텍스트 모드를 설정하지 않아 기본 모드인 MODE_THREADLOCAL 로 동작하기에 값이 없다.

InitializingBean 빈을 구현하면, 스프링이 컨테이너를 초기화하는 과정에 호출해준다.
정상적으로 값이 나온다.
주의할 것은 이 방법은 선언적으로 작성한 코드에 대해서만 동작을 한다.
선언적으로 작성한 코드는 프레임워크에서 런타임 중에 비동기임을 알기 때문에 자동으로 처리가 된다.
개발자가 메서드 안에서 코드로 쓰레드를 만들어 호출하면, 프레임워크는 비동기가 발생한지 알 수 없어, Null 이 나오게 된다.
MODE_GLOBAL
보안 컨텍스트가 모든 스레드에 공유된다.
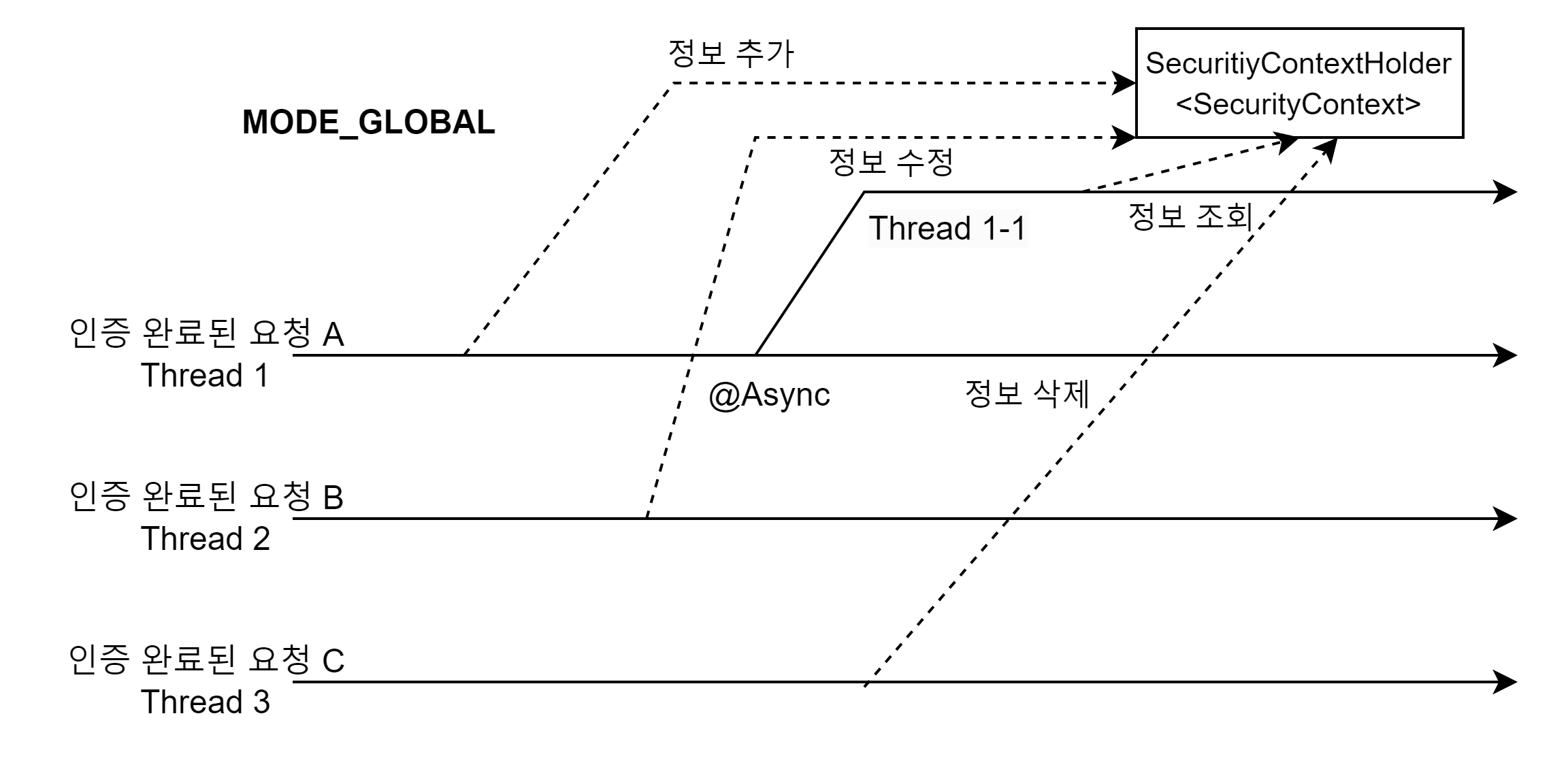
모든 스레드가 공유하기 때문에 이게 따른 동시성 이슈를 개발자가 직접 해결해야 한다.
DelegatingSecurityContextRunnable 보안 컨텍스트 전달
보안 컨텍스트 저장 전략은 총 세 가지로 그 중 기본 모드는 MODE_THREADLOCAL 이다
이 모드는 하나의 요청 마다 새로운 쓰레드를 사용하는 보편적인 서버에서 사용된다.
이 상황에서 비동기 작업을 하는 경우, 개발자가 직접 새 쓰레드로 보안 컨텍스트를 전파하는 작업을 해줘야 한다
이를 위해 스프링이 제공하는 유틸들이 있다.
DelegatingSecurityContextRunnable 은 반환 값이 없는 경우 사용
DelegatingSecurityContextCallable 은 반환 값이 있는 경우 사용한다.


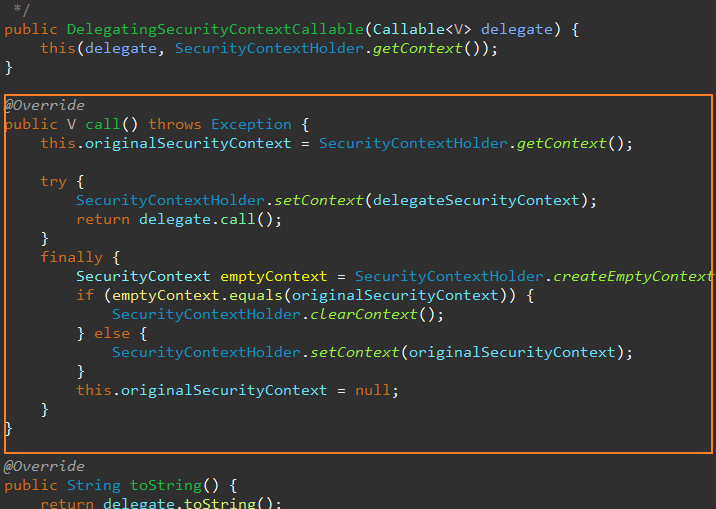
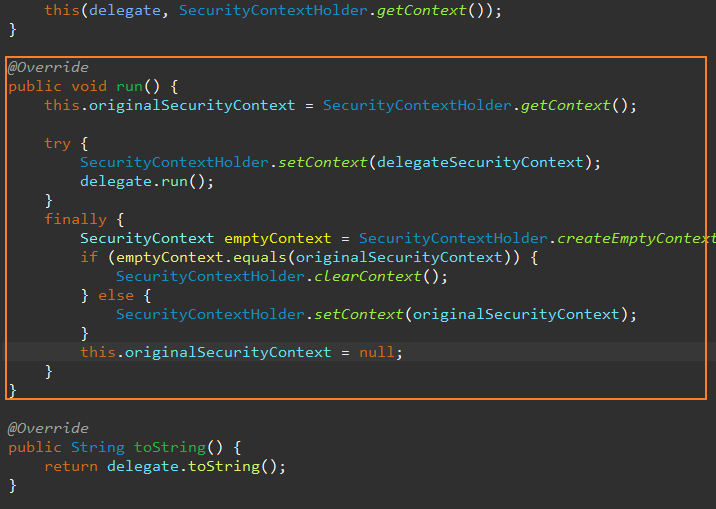
비동기 작업을 각 각 비동기 메서드를 통해, 새 쓰레드로 복사한 후 실행한다.
실행
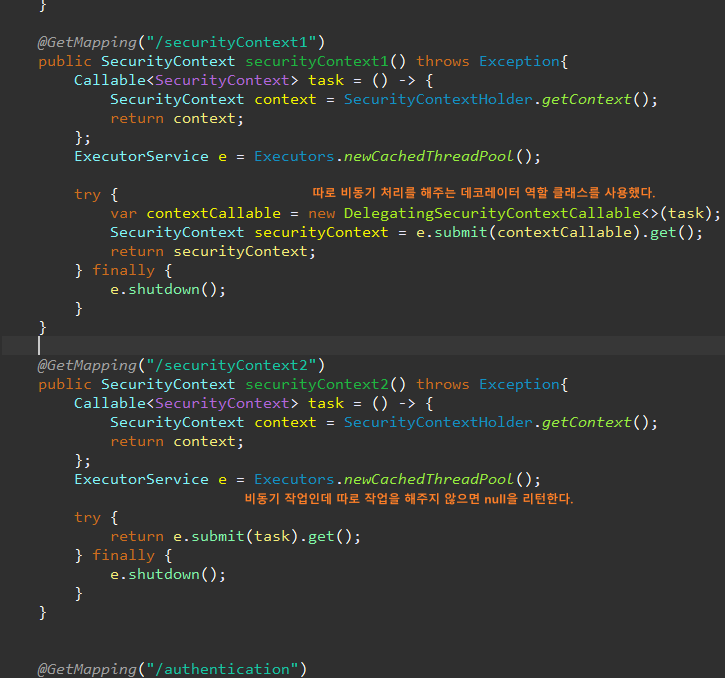
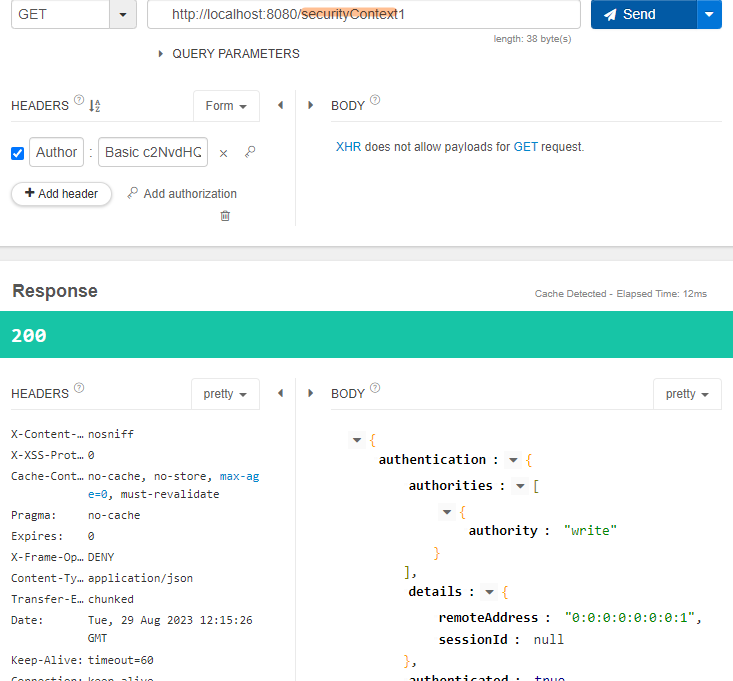
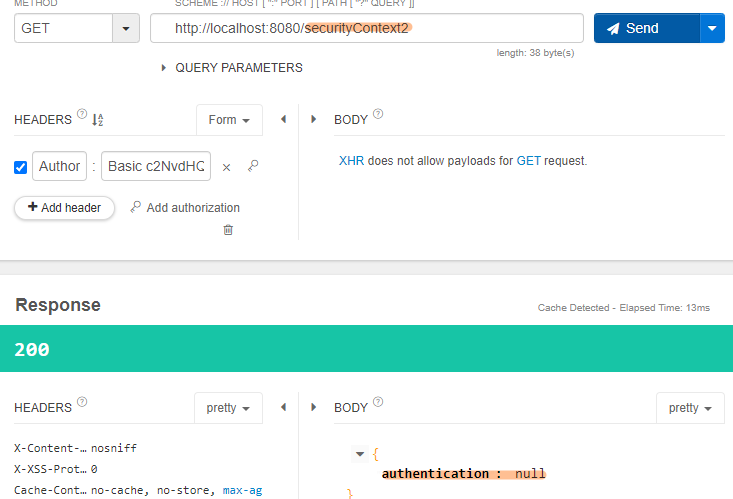
DelegatingSecurityContextExecutorService
DelegatingSecurityContextCallable, DelegatingSecurityContextRunnable은 동기화 모드에서 비동기 메서드를 사용해야 할 때 보안 컨텍스트를 복사해주는 유용한 클래스다.
이보다 더 우아한 방법으로 DelegatingSecurityContextExecutorService는 스레드 풀에서 이 전파 작업을 해준다.
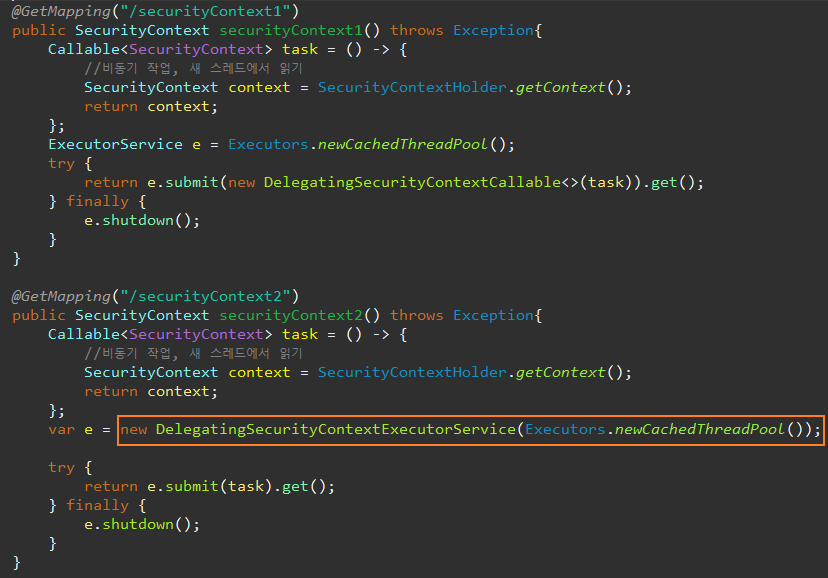
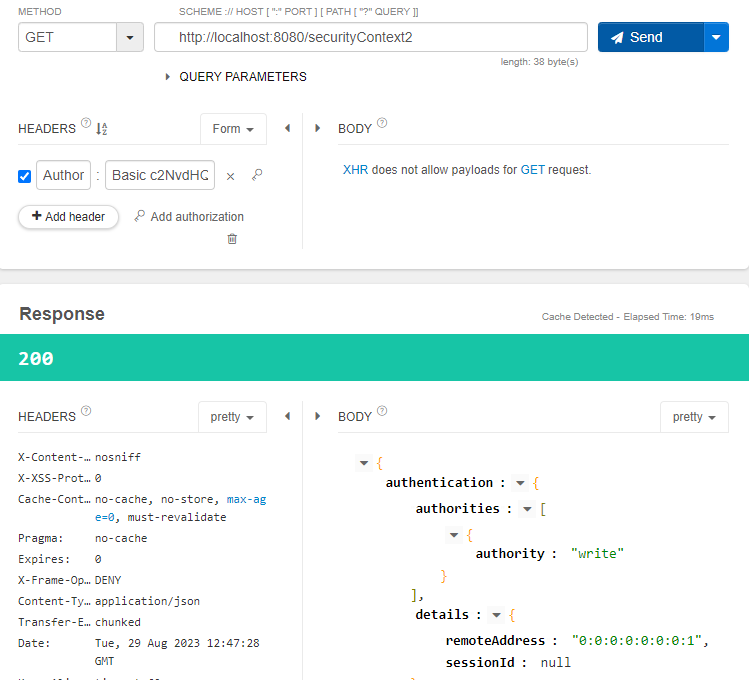
스레드 풀에서 각 새로운 스레드에 보안 컨텍스트를 전파해 준다.
이것도 기존 클래스에 기능을 더 한 데코레이터 패턴이 적용된 클래스다.
보안 컨텍스트를 전파해주는 스레드 풀 클래스
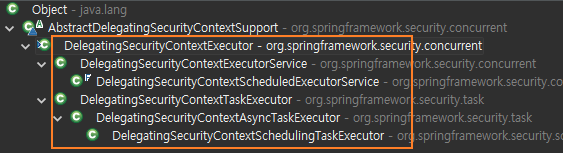
보안 컨텍스트를 전파해주는 클래스
DelegatingSecurityContextCallable, DelegatingSecurityContextRunnable
인증 실패 제어
클라이언트가 인증에 실패하거나, 액세스 권한이 없는 리소스에 인증되지 않은 요청을 하는 경우가 있다.
이 경우 클라이언트로부터 자격 증명을 요청하는 데 AuthenticationEntryPoint 구현이 사용된다.
AuthenticationEntryPoint 구현은 로그인 페이지로 리디렉션을 수행하거나, WWW-Authenticate 헤더로 응답하거나, 다른 작업을 수행할 수 있다.
일반적으로 ExceptionTranslationFilter에 인증 체계를 시작하기 전에 호출된다.
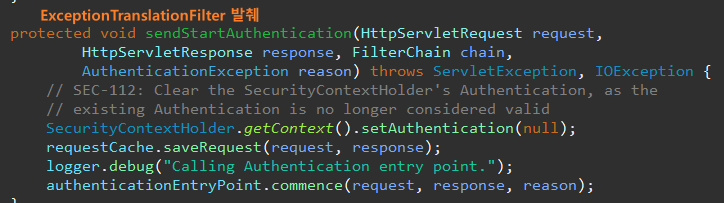
| import java.io.IOException; import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus; import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException; import org.springframework.security.web.AuthenticationEntryPoint; import jakarta.servlet.ServletException; import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; public class CustomAuthenticationEntryPoint implements AuthenticationEntryPoint{ @Override public void commence(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException authException) throws IOException, ServletException { response.addHeader("message", "Authentication Failed"); response.setStatus(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED.value()); } } |
| import javax.sql.DataSource; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService; import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.NoOpPasswordEncoder; import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder; import org.springframework.security.provisioning.JdbcUserDetailsManager; import org.springframework.security.web.SecurityFilterChain; import com.springsecurity.authentication.CustomAuthenticationEntryPoint; @Configuration public class SecurityConfig { @Bean SecurityFilterChain config(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http.httpBasic(c -> { c.realmName("ADMIN"); c.authenticationEntryPoint(new CustomAuthenticationEntryPoint()); }); http.authorizeHttpRequests(request -> { request.anyRequest().authenticated(); }); return http.build(); } @Bean PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() { return NoOpPasswordEncoder.getInstance(); } @Bean UserDetailsService userDetailsService(DataSource dataSource) { return new JdbcUserDetailsManager(dataSource); } } |
인증 실패 해보기
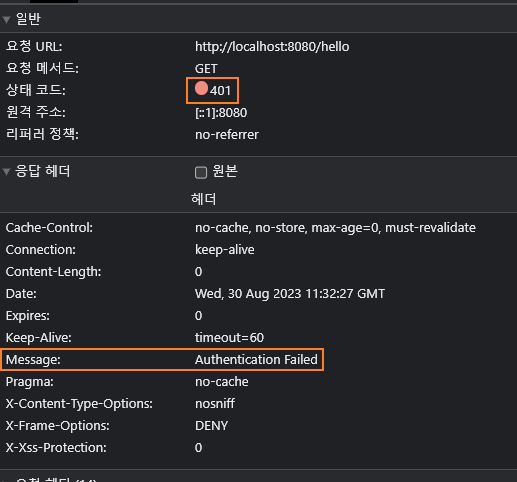
Form 기반 로그인 인증 구현
일반적인 사용자가 ID/PW 를 입력해서, 인증하는 방식을 실습해본다.
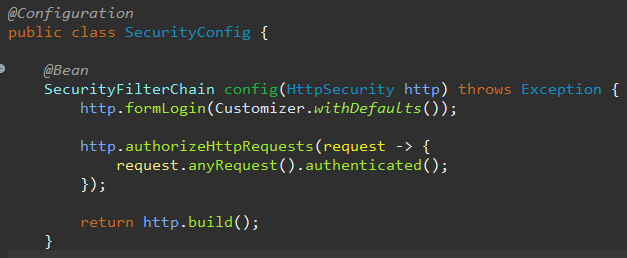
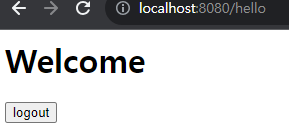
위와 같이 설정 후 서버를 키고 접속하면, 스프링이 기본으로 제공하는 로그인 페이지가 뜬다.
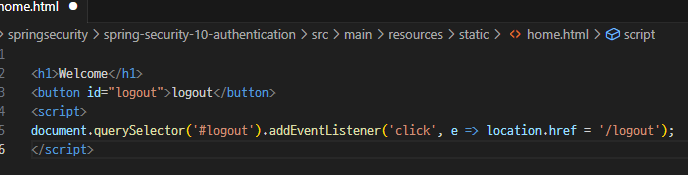
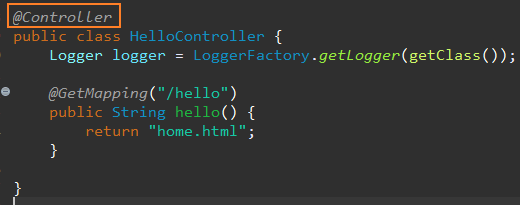
이전처럼 RestController가 아닌 일반 Controller로 실습을 하기 위해 간단한 html파일 생성
폼 로그인 성공/실패 시 처리할 핸들러
성공은 AuthenticationSuccessHandler, 실패는 AuthenticationFailureHandler 를
각각 구현해서 아래에 메서드에 등록해 주면 된다.
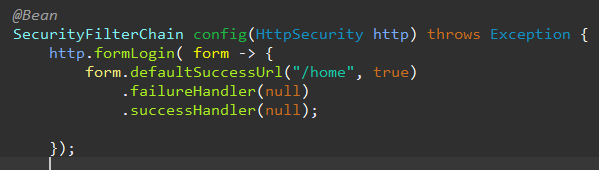
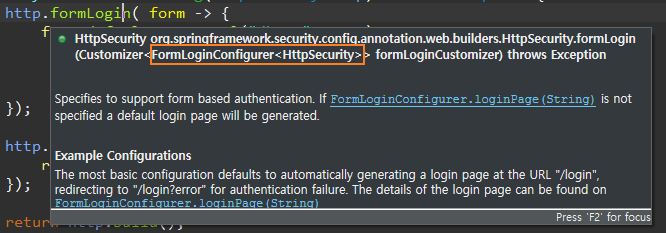
form 타입은 FormLoginConfigurer<HttpSecurity>으로 양식 인증 관련 다양한 설정을 할 수 있다.
AuthenticationSuccessHandler, AuthenticationFailureHandler 구현
| import java.io.IOException; import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication; import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.AuthenticationSuccessHandler; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import jakarta.servlet.ServletException; import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; @Component public class CustomAuthenticationSuccessHandler implements AuthenticationSuccessHandler{ public void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authentication) throws IOException, ServletException { var auth = authentication.getAuthorities() .stream() .filter(a -> a.getAuthority().equals("read")) .findFirst(); if(auth.isEmpty()) { //권한 없음 response.sendRedirect("/error"); } else { //권한 존재 response.sendRedirect("/home"); } } } |
| import java.io.IOException; import java.time.LocalDateTime; import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException; import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.AuthenticationFailureHandler; import jakarta.servlet.ServletException; import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; public class CustomAuthenticationFailureHandler implements AuthenticationFailureHandler{ @Override public void onAuthenticationFailure(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException exception) throws IOException, ServletException { response.addHeader("failed", LocalDateTime.now().toString()); } } |
| import java.io.IOException; import java.time.LocalDateTime; import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException; import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.AuthenticationFailureHandler; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import jakarta.servlet.ServletException; import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; @Component public class CustomAuthenticationFailureHandler implements AuthenticationFailureHandler{ public void onAuthenticationFailure(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException exception) throws IOException, ServletException { response.addHeader("failed", LocalDateTime.now().toString()); } } |
| import java.io.IOException; import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus; import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException; import org.springframework.security.web.AuthenticationEntryPoint; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import jakarta.servlet.ServletException; import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; @Component public class CustomAuthenticationEntryPoint implements AuthenticationEntryPoint{ public void commence(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException authException) throws IOException, ServletException { response.addHeader("message", "Authentication Failed"); response.setStatus(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED.value()); } } |
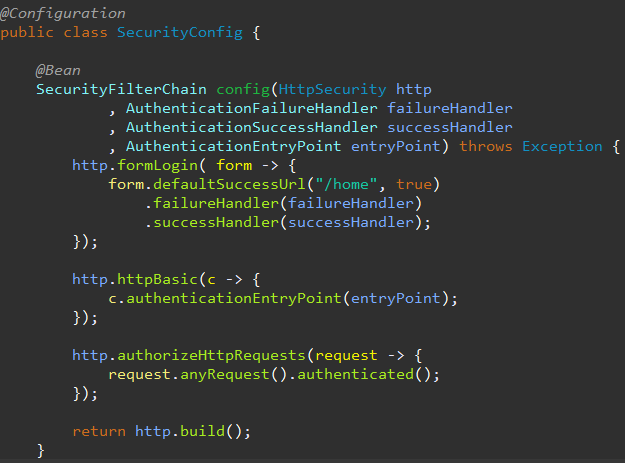
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity를 가져옵니다.
org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService 가져오기;
org.springframework.security.crypto.password.NoOpPasswordEncoder 가져오기;
org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder 가져오기;
org.springframework.security.provisioning.JdbcUserDetailsManager 가져오기;
org.springframework.security.web.SecurityFilterChain 가져오기;
import com.springsecurity.authentication.CustomAuthenticationEntryPoint;
@구성
공개 클래스 SecurityConfig {
@콩
SecurityFilterChain 구성(HttpSecurity http)에서 예외가 발생합니다.
http.http기본(c -> {
c.realmName("관리자");
c.authenticationEntryPoint(new CustomAuthenticationEntryPoint());
});
http.authorizeHttpRequests(요청 -> {
request.anyRequest().authenticated();
});
http.build()를 반환합니다.
}
@콩
PasswordEncoder 비밀번호Encoder() {
NoOpPasswordEncoder.getInstance()를 반환합니다.
}
@콩
UserDetailsService userDetailsService(DataSource dataSource) {
새로운 JdbcUserDetailsManager(dataSource)를 반환합니다.
}
}
'개발 > 스프링 시큐리티' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 스프링 시큐리티 인 액션 - 암호 처리 (0) | 2023.09.01 |
|---|---|
| 스프링 시큐리티 인 액션 - 사용자 관리 (0) | 2023.08.30 |
| 스프링 시큐리티 인 액션 - 안녕! 스프링 시큐리티 (0) | 2023.08.23 |
| 스프링 시큐리티 인증 아키텍처 (0) | 2023.08.17 |
| 스프링 시큐리티 인 액션 - 오늘날의 보안 (0) | 2023.08.15 |